How real-time vehicle data boosts fleet performance
Jun 9, 2025 Resolute Dynamics

Fleet management isn’t just about keeping wheels turning—it’s about making every trip count. Real-time data is changing the game, giving operators a clear view of fuel use, driving habits, and more. With those insights, they can slash risks, lower costs, and run a tighter, smarter operation.
Let’s explore how this technology works and why it’s become essential for modern fleet management.
✅Key Takeaway:
Live data shows managers exactly how drivers move, how vehicles perform, and where fuel goes. That means fewer breakdowns, smaller bills, and safer crews. No more waiting for trouble—decisions come quicker, and the whole system runs sharper.
Why Real-Time Data Is a Game Changer for Fleets

Fleet management used to be all clipboards, static GPS, and waiting for things to break. Now, real-time data changes the playbook. You get live insights—where vehicles are, how they’re driven, and early warning signs before small issues turn into big, costly problems.
Why wait for trouble to show up? Real-time insights help fleet managers stay ahead—make quicker decisions, tighten safety, and keep things humming. Fewer roadside shocks mean better control over the budget and a lot less stress.
What Is Real-Time Vehicle Data and How Is It Collected?
Real-time vehicle data is a live feed pulled straight from a vehicle’s sensors and systems while it’s moving. This stream gets processed and sent out in milliseconds, giving fleet managers instant visibility into performance, driver habits, and mechanical health—no lag, no guesswork.
To really grasp how it all works, you’ve got to break it down—where the data comes from, how it’s gathered, and how it’s delivered.
Core Data Sources in Real-Time Vehicle Monitoring
-
Global Positioning System (GPS) Modules
GPS trackers constantly update a vehicle’s location, speed, and heading. They provide:-
Real-time location tracking for route planning
-
Geofencing to alert if a vehicle enters or leaves a designated area
-
Historical trip replay for analysis
-
-
On-Board Diagnostics (OBD-II) & CAN Bus Systems
The OBD-II port taps into a vehicle’s engine control unit (ECU). In today’s fleets, it links to the CAN bus—an internal network that lets key systems like brakes, fuel, emissions, and transmission talk to each other in real time.
Key data points include:
-
Engine temperature, RPM, throttle position
-
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
-
Battery voltage and oil pressure
-
Fuel economy and emissions data
-
-
Accelerometers and Gyroscopes
These motion sensors measure forces like sudden braking, harsh cornering, or rollover risk. They provide granular details on:-
Driver behavior profiling
-
Accident reconstruction
-
G-force events and safety violations
-
-
AI-Based Dash Cameras and ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance Systems)
Cameras integrated with AI and machine vision capture the driver’s actions and external environment. These systems detect:-
Lane departures
-
Traffic signs and obstacles
-
Distracted or drowsy driving
-
Collision warnings
-
-
Fuel Monitoring Sensors and IoT Devices
These track fuel levels, refill patterns, and potential fuel theft. Integrated IoT sensors may also capture tire pressure, load weight, and temperature for cold-chain logistics.
How Real-Time Vehicle Data Is Collected
The moment a vehicle engine starts, sensors and systems begin capturing data. The collection process typically involves:
-
Edge Computing: Some telematics units perform data processing locally (on the device) to reduce the volume of transmitted data and enable immediate alerts (e.g., if the engine overheats).
-
Wireless Transmission: The collected data is transmitted via cellular networks (3G/4G/5G), satellite, or Wi-Fi to centralized servers or cloud platforms.
-
Vehicle Telematics Control Units (TCUs): These black-box devices act as central hubs inside each vehicle. They aggregate data from all sources—GPS, OBD, cameras, and sensors—and encrypt it before transmission.
How Fleet Managers Use This Data
Once the data reaches the fleet management software or Vehicle Intelligence Platform (VIP), it’s visualized in dashboards. Fleet operators get:
-
Live map views of all vehicles
-
Alerts for speed violations, maintenance needs, and unsafe driving
-
Performance analytics for routes, drivers, and fuel usage
-
Predictive insights based on behavior patterns
With our real-time telematics and data intelligence platform, these insights go a step further—transforming raw sensor data into live, actionable intelligence that helps fleet managers make smarter, faster, and safer decisions on the road.
The entire ecosystem works in real time—every signal is captured, assessed, and used to make faster, smarter decisions.
Real-World Example: AI-Powered Telematics
For example, Resolute Dynamics uses a multi-layered telematics architecture:
-
Their Connect system transmits and analyzes live vehicle data globally.
-
Combined with Capture (AI vision systems) and Control (speed and behavior management), the fleet becomes an intelligent, self-correcting network.
These AI-driven speed and behavior management systems ensure that every vehicle adapts dynamically to real-time road and traffic conditions, optimizing compliance, safety, and fuel efficiency across the entire fleet. -
Over 200,000 vehicles across the UAE, MENA, and Asia use their system to reduce collisions, manage fuel costs, and enforce safety compliance—all through real-time vehicle data.
Key Benefits of Real-Time Vehicle Data for Fleet Operators

1. Improved Safety and Compliance
AI-driven systems spot danger signs—tailgating, swerving, or nodding off—before they turn into trouble. Instant alerts give drivers a chance to fix it fast. It’s not just about safety on the road—it also helps companies stay on the right side of laws and industry rules.
Smart systems use geofencing to control speed automatically, keeping fleets within legal limits—no need for constant oversight or micromanaging from dispatch.
2. Enhanced Operational Efficiency
With real-time traffic and vehicle data, dispatchers can steer drivers away from jams and hold-ups on the fly. Telematics goes further—crunching trip info to spot fuel-saving routes, cut idle time, and ease the strain on your vehicles over the long haul.
When things run this smoothly, deliveries hit the mark—and customers notice the difference in service quality.
3. Fuel Cost Reduction
Fuel eats up a big chunk of any fleet’s budget. Live data can flag wasteful habits—like long idling, hard takeoffs, or sloppy routing. Tweak those behaviors, and you’re not just saving cents—you’re trimming thousands off the fuel bill over time.
These systems also track tire pressure and vehicle load—quiet fuel wasters that often slip under the radar but add up fast.
4. Predictive Maintenance
One of the biggest wins with real-time data? Catching problems before they sideline a vehicle. Engine scans and sensor data flag early signs of trouble—like heat spikes, worn brakes, or gear issues—giving fleets time to fix things before they snowball.
It lets fleet managers plan ahead—scheduling maintenance before things break down and sidestepping costly roadside surprises and repairs.
Case Study: Resolute Dynamics’ Real-Time Fleet Solutions
Resolute Dynamics offers advanced AI-powered systems built specifically for fleet performance and road safety. Their technology is used in over 200,000 vehicles across 20+ countries, including the UAE, India, and Southeast Asia.
Their platform includes:
-
Capture: AI vision systems to monitor road conditions and driver behavior
-
Connect: Telematics that turn raw data into actionable insights
-
Control: Intelligent systems that optimize vehicle speed, fuel use, and safety compliance
These tools help fleet operators respond in real time to changing road conditions, unsafe actions, or potential maintenance issues—maximizing efficiency and minimizing risks.
How AI and Machine Learning Supercharge Fleet Data
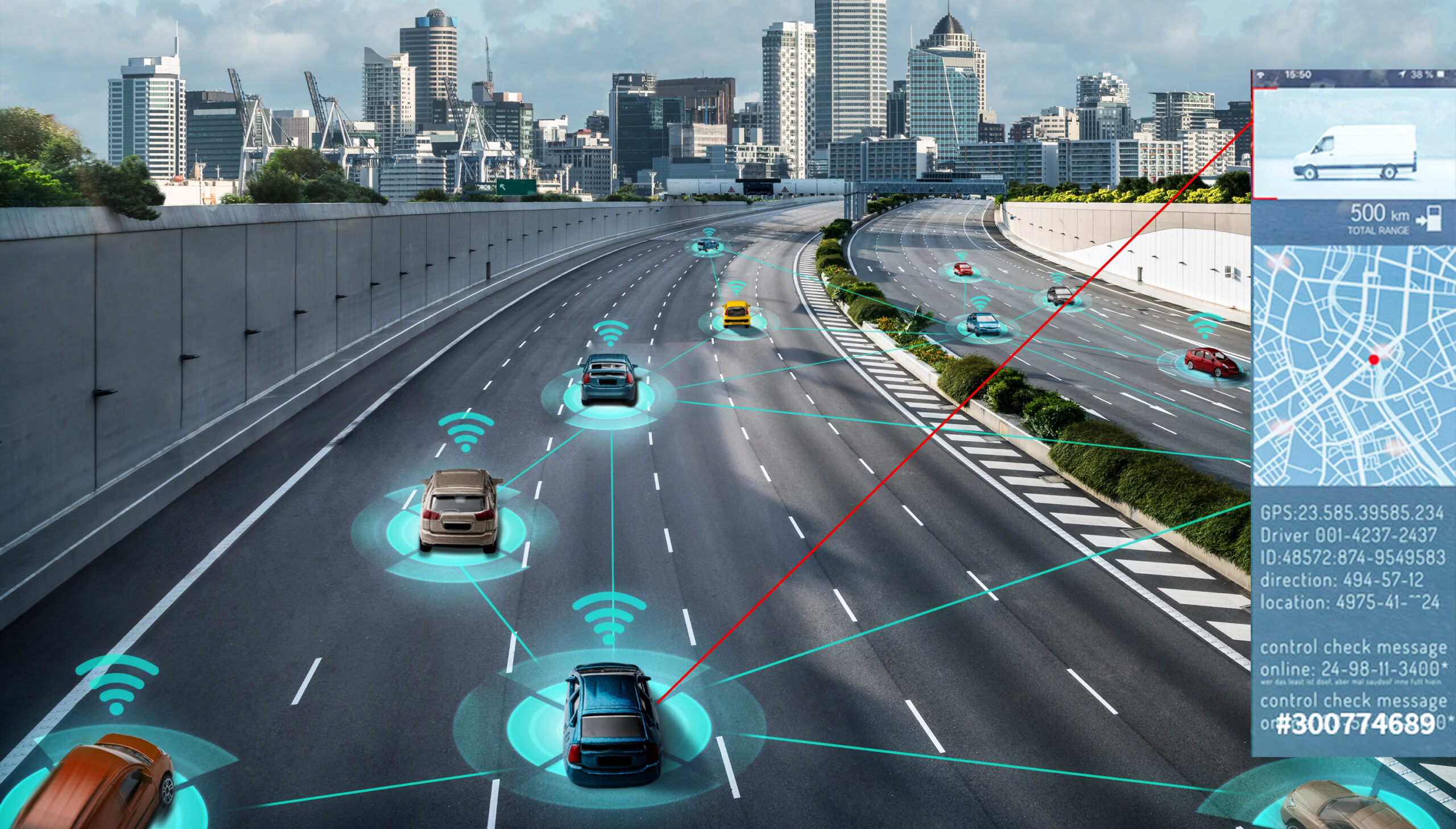
A connected fleet’s value isn’t in the data—it’s in the action that follows. AI and Machine Learning turn raw numbers into live insights fleet managers can use on the spot. This isn’t just about tracking—it’s about spotting trends, predicting issues, and keeping operations one step ahead, always.
Understanding the Role of AI in Fleet Management
AI works like the brain behind the wheel, crunching everything from engine stats to traffic flow. It pulls meaning from messy data—a process called inference—so systems can spot odd patterns, read the situation, and offer up smarter next steps.
Here’s how AI makes sense of telematics data:
-
Identifies unsafe driving patterns over time
-
Flags underperforming routes or assets
-
Recommends preventive maintenance based on usage behavior
-
Optimizes delivery schedules based on historical performance
For example, if a driver consistently brakes harshly or idles longer than others, the AI system can flag this and suggest driver coaching or training.
What Machine Learning Actually Does
Machine Learning is a branch of AI that gets smarter with use. It studies past data, adjusts its patterns, and fine-tunes itself as new information rolls in.
In fleet analytics, ML models are trained on:
-
Thousands of driving hours
-
Vehicle component wear-and-tear data
-
Traffic flow patterns
-
Fuel efficiency metrics
-
Environmental variables like road surface or temperature
Once trained, these models predict:
-
When a vehicle might break down (predictive maintenance)
-
Which driver is most at risk of causing an incident (risk profiling)
-
Which routes will be most fuel-efficient at specific times
-
The probability of delivery delays due to congestion or roadblocks
This predictive capability allows for preemptive decision-making—the holy grail of operational efficiency.
Key AI/ML Applications in Fleet Data Ecosystems
| Use Case | How AI/ML Helps |
|---|---|
| Driver Behavior Monitoring | Scores drivers based on acceleration, braking, and fatigue indicators. Identifies high-risk individuals. |
| Predictive Maintenance | Detects anomalies in sensor data to forecast part failures before they happen. |
| Route Optimization | Learns which routes are faster or more fuel-efficient under different conditions. |
| Fuel Efficiency Optimization | Tracks fuel burn vs. load vs. terrain to optimize consumption patterns. |
| Safety Risk Modeling | Predicts chances of incidents based on environmental and behavioral data. |
| Autonomous Fleet Support | Feeds data into Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) to improve automated decision-making. |
AI Algorithms Used in Telematics Platforms
-
Regression Analysis: Used to forecast fuel usage or maintenance timelines
-
Anomaly Detection: Flags unusual data like a sudden spike in engine temperature
-
Clustering: Groups similar driving behaviors or route patterns to simplify reporting
-
Classification Models: Categorizes drivers into risk levels or identifies high-efficiency vehicles
-
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Converts driver comments or maintenance logs into actionable data
These models become more accurate over time as they ingest more data—this is called model training and reinforcement learning.
Real-World Example: AI in Resolute Dynamics’ Fleet Platform
Resolute Dynamics integrates machine learning across its Capture, Connect, and Control framework:
-
Capture uses AI vision systems to understand the road environment and driver actions.
-
Connect leverages ML models to spot inefficiencies in real-time data and predict outcomes.
-
Control adapts vehicle behavior (like speed and fuel throttle) to optimize performance.
This closed-loop system transforms every data point into actionable insight—enhancing safety, efficiency, and profitability across 200,000+ vehicles globally.
Real-Time Alerts: Making Decisions When It Matters Most
From congested city streets to open highways, real-time alerts help drivers and managers stay ahead of problems. Whether it’s an engine warning light or a sudden slowdown ahead, alerts are sent immediately so action can be taken.
These alerts reduce response times, improve safety, and help avoid unnecessary downtime.
Data Privacy and Compliance Considerations
Handling real-time vehicle data comes with responsibility. Companies must follow strict privacy and cybersecurity rules to protect driver and vehicle data.
This includes encryption, data anonymization, and compliance with regional laws like GDPR or UAE’s cybersecurity framework. A secure system builds trust with drivers and ensures legal compliance across borders.
Future Trends in Fleet Telematics and Real-Time Data
The future of fleet management is hyper-connected. Telematics will soon integrate with smart cities and V2X (vehicle-to-everything) communication. Vehicles will talk to traffic lights, road signs, and even other cars to avoid collisions and optimize traffic flow.
We’ll also see more automation, including autonomous delivery vehicles and self-monitoring fleets that manage themselves with minimal human input.
Conclusion: From Data to Decisions—Driving Smarter Fleets
Real-time vehicle data isn’t just helpful—it’s essential for fleets aiming to stay sharp, safe, and in the black. It flips the script from reacting to predicting, turning daily routes into data-driven moves that actually make a difference.
Fleet operators who embrace real-time insights are not only improving today’s performance—they’re shaping the future of transportation.